When to see your dentist
If you have toothache for longer than one or two days, you should visit your dentist as soon as possible to have it treated. The longer you leave it, the worse it will get. If your toothache is not treated, the tooth will eventually become infected. This usually leads to an abscess forming, which can cause severe and continuous pain. Painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen may help reduce pain and discomfort while you are waiting for an appointment. Children under 12 years of age should not be given aspirin. Please seek medical advice before taking any medication.
Why it happens
Toothache happens as a result of:
- tooth decay
- a cracked tooth
- lose or broken fillings
- receeding gums
- an abscess
There are a number of other conditions that can cause pain similar to toothache, even though the tooth is not affected. These include:
- periodontal abscess
- ulcers on your gums
- wisdom tooth pain
- sinusitis
- jaw joint pain
What can I do before seeing the dentist?
Although a toothache means a trip to your dentist, you can ease your pain beforehand. Rinse your mouth with warm salt water to clean it. Then, using dental floss, gently try to remove any food particles or other debris wedged between your teeth, taking care to avoid cutting your gums. (Never use a sharp instrument to dislodge an object stuck between your teeth; this can cause bleeding and worsen your pain. Allow your dentist to remove it.)
Avoid putting aspirin or any other painkiller directly against your gums – it might burn delicate gum tissue. Instead, try a cold compress or ice wrapped in cloth to the outside of the cheek, especially if there’s any swelling around the tooth.
Dental Trauma
What to do in case of a fall that affects a permanent tooth?
First, you must consult a dentist immediately after the accident has occurred. Doing so means:
- There is more possibility of conserving the tooth’s vitality (life)
- A conservation treatment will be applied.
- There is a better prognosis.
- Future complications and high cost treatments are prevented.
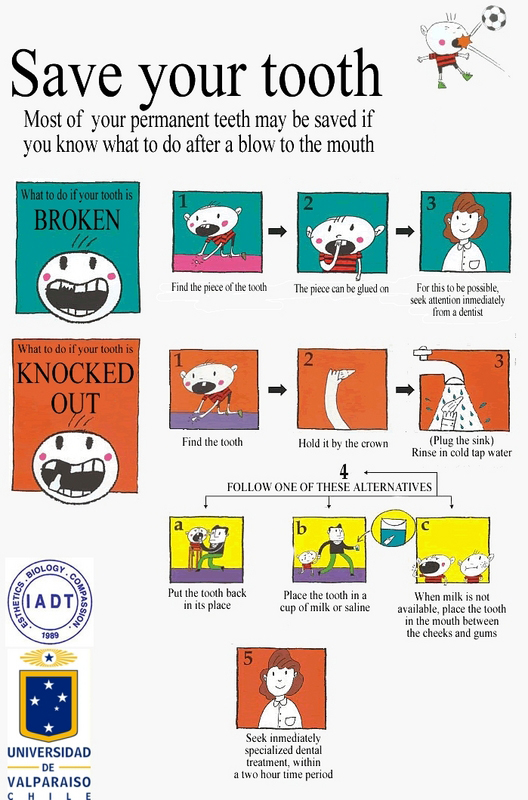
What to do if a permanent tooth is broken or knocked out?
If a tooth is avulsed, make sure it is a permanent tooth (primary teeth should not be replanted).
- Find the tooth. Hold the tooth by the crown (the white part), not by the root (the yellow part).
- Replant immediately, if possible.
- If contaminated, rinse for 10 seconds with cold tap water and put the tooth back in its place. This can be done by the child or an adult.
- Hold the tooth in place. Bite on a handkerchief to hold it in position and go to the dentist immediately.
- If you cannot put the tooth back in, place it in a cup of milk or saline. When milk or saline are not available, place the tooth in the child’s mouth (between the cheeks and gums). If the patient is very young, he/she could swallow the tooth- therefore it is advisable to get the patient to spit in a container and place the tooth in it. Avoid storage in water!
- Seek emergency dental treatment immediately.
SEE poster